Apprenticeships 2025: Redefining US Vocational Education

The US is experiencing a transformative phase in vocational education, as apprenticeships are increasingly recognized as pivotal in bridging skill gaps and preparing a future-ready workforce across key sectors by 2025.
The landscape of education and workforce development in the United States is undergoing a profound transformation, with a renewed focus on practical, hands-on learning. At the forefront of this evolution is US Apprenticeship Redefinition, a movement that is swiftly gaining momentum as industries recognize the unparalleled value of combining theoretical knowledge with real-world application. This shift is not merely a trend but a strategic imperative, designed to address critical skill gaps and prepare a robust workforce for the demands of 2025 and beyond.
The evolving role of apprenticeships in modern education
Apprenticeships, once largely associated with traditional trades, are experiencing a significant resurgence, broadening their scope across an array of modern industries. This evolution reflects a growing understanding that traditional academic paths alone cannot meet the dynamic demands of today’s job market. The modern apprenticeship model integrates classroom instruction with on-the-job training, providing participants with both theoretical foundations and practical competencies.
This blended learning approach offers numerous advantages over conventional educational models. Apprentices gain valuable work experience while earning a wage, often avoiding the burden of student debt. For employers, apprenticeships serve as a powerful tool for talent acquisition and development, allowing them to cultivate a highly skilled workforce tailored to their specific needs. This symbiotic relationship fosters a more responsive and adaptable labor market.
Bridging the skill gap with practical training
One of the most compelling arguments for the expansion of apprenticeships is their effectiveness in addressing the persistent skill gap. Many industries face challenges in finding candidates with the specific competencies required for contemporary roles. Apprenticeship programs are designed to close this gap by:
- Providing targeted training that aligns directly with industry demands.
- Allowing for continuous adaptation of curriculum to emerging technologies.
- Developing soft skills such as problem-solving, teamwork, and communication.
The structured nature of these programs ensures that apprentices receive comprehensive instruction, not just in technical skills but also in the professional attributes essential for long-term career success. This holistic development is crucial for building a resilient and future-proof workforce.
Furthermore, the investment in apprenticeships signals a commitment to cultivating local talent pools, reducing reliance on external recruitment, and strengthening community economies. As more businesses embrace this model, the collective impact on national workforce readiness becomes increasingly significant, paving the way for sustained economic growth and innovation.
Healthcare: pioneering new pathways to patient care
The healthcare sector is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, an aging population, and evolving patient needs. In response, apprenticeships are emerging as a vital strategy to build a skilled and adaptable healthcare workforce. These programs are addressing critical shortages in various roles, from medical assistants and surgical technicians to specialized roles in health informatics.
Traditionally, many healthcare professions required extensive university degrees, which could be costly and time-consuming. Modern healthcare apprenticeships offer an alternative by combining paid work experience with structured learning, enabling individuals to enter the field more quickly and affordably. This approach not only diversifies the talent pipeline but also ensures that new professionals are immediately productive upon qualification.
Addressing staffing shortages through innovative programs
Healthcare institutions across the US are leveraging apprenticeships to directly tackle chronic staffing shortages. These programs are often developed in partnership with educational institutions and local workforce boards, ensuring that the training provided is both academically rigorous and clinically relevant. For example, some hospitals are implementing apprenticeship models for:
- Certified nursing assistants (CNAs) and licensed practical nurses (LPNs).
- Medical coders and billers, essential for administrative efficiency.
- Pharmacy technicians, supporting critical medication management.
These initiatives not only provide immediate staffing relief but also create clear career progression pathways for apprentices. This structure encourages retention and continuous professional development, which are crucial for maintaining high-quality patient care in a demanding environment.
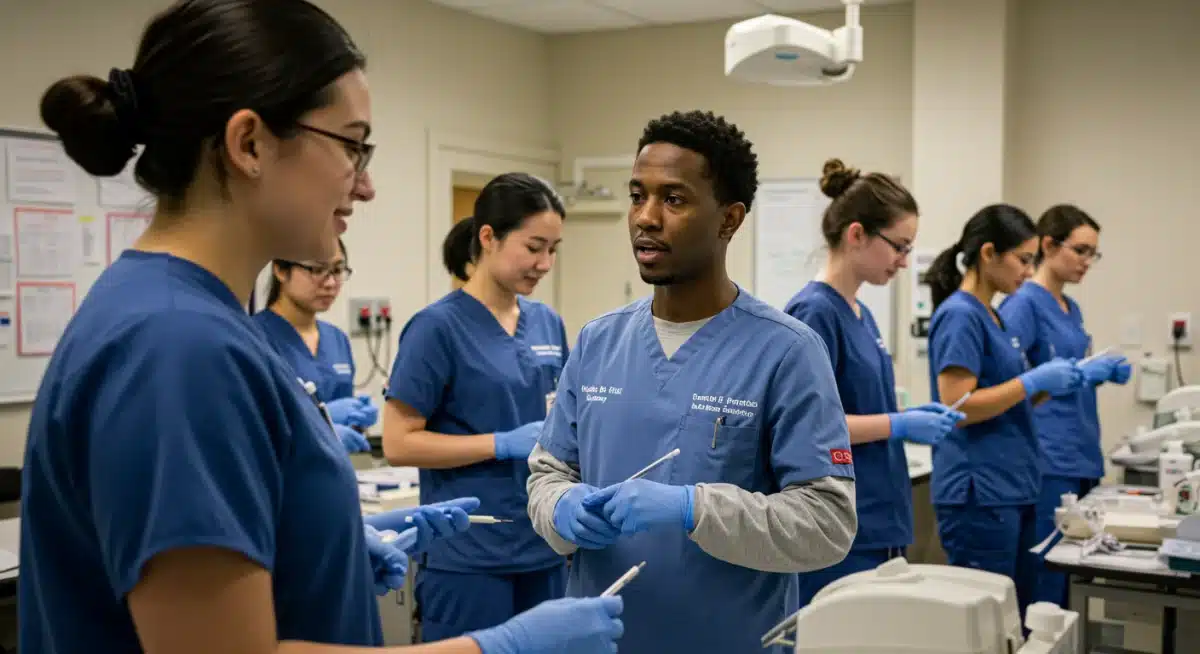
The integration of apprenticeships into healthcare education is proving to be a game-changer. It allows for a more fluid response to workforce needs and ensures that the next generation of healthcare professionals is equipped with both the knowledge and the practical experience necessary to excel in complex clinical settings. This model is critical for sustaining and improving healthcare services nationwide.
Information technology: fueling the digital economy with skilled talent
The information technology (IT) sector is perhaps one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving industries, characterized by constant innovation and an insatiable demand for specialized skills. In this environment, traditional educational models often struggle to keep pace with technological advancements. Consequently, IT apprenticeships have become an indispensable tool for developing a workforce that is not only current but also future-ready.
IT apprenticeships offer a practical pathway into high-demand roles, such as cybersecurity analysts, software developers, data scientists, and network engineers. These programs are particularly attractive because they provide hands-on experience with cutting-edge technologies and methodologies, which is often difficult to replicate in a purely academic setting. Apprentices learn directly from experienced professionals, gaining insights and skills that are immediately applicable in the workplace.
Cultivating specialized tech skills for tomorrow
The complexity of modern IT roles necessitates highly specialized training. Apprenticeship programs are uniquely positioned to deliver this by focusing on niche areas that are critical to business success. Key areas where IT apprenticeships are making a significant impact include:
- Cybersecurity: Training in threat detection, incident response, and network security protocols.
- Software Development: Practical experience in various programming languages, agile methodologies, and full-stack development.
- Data Analytics: Instruction in data visualization, statistical analysis, and machine learning applications.
These programs not only equip individuals with technical proficiency but also foster critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, which are paramount in the fast-paced tech world. The ability to adapt and learn new technologies on the fly is a core competency developed through these immersive experiences.
Furthermore, IT apprenticeships are helping to diversify the tech workforce by providing opportunities to individuals from non-traditional backgrounds, including those without a four-year degree. This inclusivity broadens the talent pool and brings new perspectives to innovation, reinforcing the sector’s growth and competitive edge in the global digital economy.
Advanced manufacturing: innovating industry through precision training
Advanced manufacturing, a sector characterized by high-tech processes, automation, and sophisticated machinery, is another area where apprenticeships are proving transformational. As traditional manufacturing evolves into a realm demanding precision, digital literacy, and intricate problem-solving, the need for a highly skilled workforce has never been greater. Apprenticeships are directly addressing this by providing the specialized training required to operate, maintain, and innovate within modern factories.
These programs move beyond basic assembly line skills, delving into areas like robotics, additive manufacturing (3D printing), industrial controls, and quality assurance. Apprentices gain invaluable experience working with complex systems, learning to troubleshoot, optimize production, and implement new technologies. This hands-on learning environment ensures that graduates are not just job-ready but also capable of contributing to continuous improvement and innovation from day one.
Modernizing manufacturing with cutting-edge skills
The advanced manufacturing sector benefits immensely from apprenticeship models that are designed to keep pace with technological advancements. Employers can tailor programs to specific equipment and processes, ensuring that apprentices develop skills directly relevant to their operations. This includes training in:
- Robotics and Automation: Programming, operating, and maintaining industrial robots.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Manufacturing (CAM): Utilizing software for product design and production.
- Precision Machining: Operating CNC machines and other high-precision tools.
By investing in these programs, manufacturers are not only filling immediate skill gaps but also building a sustainable talent pipeline. This strategic approach helps to future-proof their operations against rapid technological shifts and ensures that the US remains competitive in global manufacturing. The precision and expertise cultivated through these apprenticeships are essential for maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency.
Government initiatives and industry partnerships: fostering growth
The growing prominence of apprenticeships in the US is not solely driven by industry demand; it is also significantly bolstered by robust government initiatives and strategic industry partnerships. Federal and state governments are increasingly recognizing apprenticeships as a cornerstone of workforce development and economic growth, leading to various funding opportunities, policy reforms, and promotional campaigns.
These governmental efforts aim to expand access to apprenticeship programs, particularly for underrepresented populations, and to encourage more employers to adopt this training model. This support often comes in the form of tax credits for businesses, grants for educational institutions developing apprenticeship curricula, and direct funding for program participants. Such initiatives reduce the financial burden on both employers and apprentices, making these programs more attractive and accessible.
Collaborative ecosystems for workforce development
The success of the modern apprenticeship movement hinges on strong collaboration between multiple stakeholders. This includes:
- Government Agencies: Providing regulatory frameworks, funding, and oversight.
- Educational Institutions: Developing related technical instruction and offering academic support.
- Industry Associations: Setting standards, advocating for sector-specific training, and connecting employers.
- Individual Employers: Offering on-the-job training, mentorship, and employment opportunities.
These partnerships create a comprehensive ecosystem that supports the entire apprenticeship journey, from recruitment and training to certification and job placement. The collective effort ensures that programs are high-quality, relevant to industry needs, and lead to recognized credentials, enhancing the value proposition for all involved parties.
Furthermore, these collaborations enable the sharing of best practices and resources, fostering a continuous improvement cycle for apprenticeship models. As these partnerships mature, they are expected to drive even greater innovation and expansion in vocational education, cementing apprenticeships as a permanent and vital component of the US workforce strategy for years to come.
The future outlook: expanding impact and accessibility
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, the trajectory for apprenticeships in the United States points towards continued expansion and diversification. The successes observed in healthcare, IT, and advanced manufacturing are serving as powerful models for other sectors, including clean energy, logistics, and even creative industries. This broad appeal is driven by the demonstrable benefits apprenticeships offer in terms of skill development, employment rates, and economic productivity.
A key focus for the future will be enhancing the accessibility and inclusivity of apprenticeship programs. Efforts are underway to reach a wider demographic, ensuring that individuals from all backgrounds, including veterans, women, and minority groups, have equitable opportunities to participate. This includes developing pre-apprenticeship programs that prepare candidates for entry into more rigorous technical training.
Integrating apprenticeships into mainstream education
The long-term vision for apprenticeships involves their deeper integration into the mainstream educational system. This means:
- Creating clearer pathways from high school to apprenticeship programs.
- Developing articulation agreements with community colleges and universities for credit transfer.
- Promoting apprenticeships as a viable and respected alternative to traditional four-year degrees.
By positioning apprenticeships as a first-choice option for career development, the US can cultivate a more diverse and skilled workforce, capable of meeting the complex challenges of the 21st century. The emphasis will remain on ensuring that these programs are responsive to economic shifts and technological advancements, guaranteeing their continued relevance and effectiveness.
Ultimately, the future of vocational education in the US is intrinsically linked to the continued rise and evolution of apprenticeships. As these programs become more sophisticated and widespread, they will not only redefine how individuals learn and work but also fundamentally reshape the economic landscape, fostering innovation and sustainable growth across all sectors.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Healthcare Sector | Apprenticeships address staffing shortages and create new pathways for roles like CNAs and medical coders, ensuring practical skill development. |
| Information Technology | IT apprenticeships fuel the digital economy by providing specialized training in cybersecurity, software development, and data analytics. |
| Advanced Manufacturing | These programs modernize manufacturing with training in robotics, CAD/CAM, and precision machining, driving innovation and efficiency. |
| Government & Partnerships | Government initiatives and industry collaborations are crucial for funding, policy support, and expanding access to apprenticeship programs. |
Frequently asked questions about US apprenticeships
The primary goal is to bridge skill gaps in crucial industries by combining on-the-job training with theoretical instruction. This approach ensures that individuals acquire both practical competencies and foundational knowledge, directly meeting employer needs and fostering career readiness.
Healthcare apprenticeships help address critical staffing shortages by training individuals in roles such as medical assistants, LPNs, and pharmacy technicians. They provide a practical, debt-free pathway into the profession, ensuring a steady supply of skilled healthcare professionals.
IT apprenticeships are crucial for filling high-demand roles like cybersecurity analysts, software developers, data scientists, and network engineers. These programs offer hands-on experience with cutting-edge technologies, making apprentices immediately valuable to tech companies.
Apprenticeships in advanced manufacturing provide precision training in robotics, automation, CAD/CAM, and CNC machining. This ensures that the workforce can operate and innovate with sophisticated machinery, maintaining the US’s competitive edge in high-tech production.
Government initiatives provide funding and policy support, while industry partnerships ensure programs are relevant and high-quality. This collaboration creates a robust ecosystem that expands access to apprenticeships, fostering economic development and a skilled workforce.
Conclusion
The resurgence and redefinition of apprenticeships across the United States mark a pivotal moment in vocational education. As industries like healthcare, information technology, and advanced manufacturing continue to evolve at an unprecedented pace, the traditional educational paradigm is being challenged. Apprenticeships, with their unique blend of theoretical learning and practical application, are proving to be an indispensable solution for bridging skill gaps, fostering innovation, and building a resilient, future-ready workforce. The collaborative efforts of government, educational institutions, and private industry are not only expanding the reach and accessibility of these programs but also cementing their role as a fundamental pillar of economic growth and individual career success in 2025 and beyond.